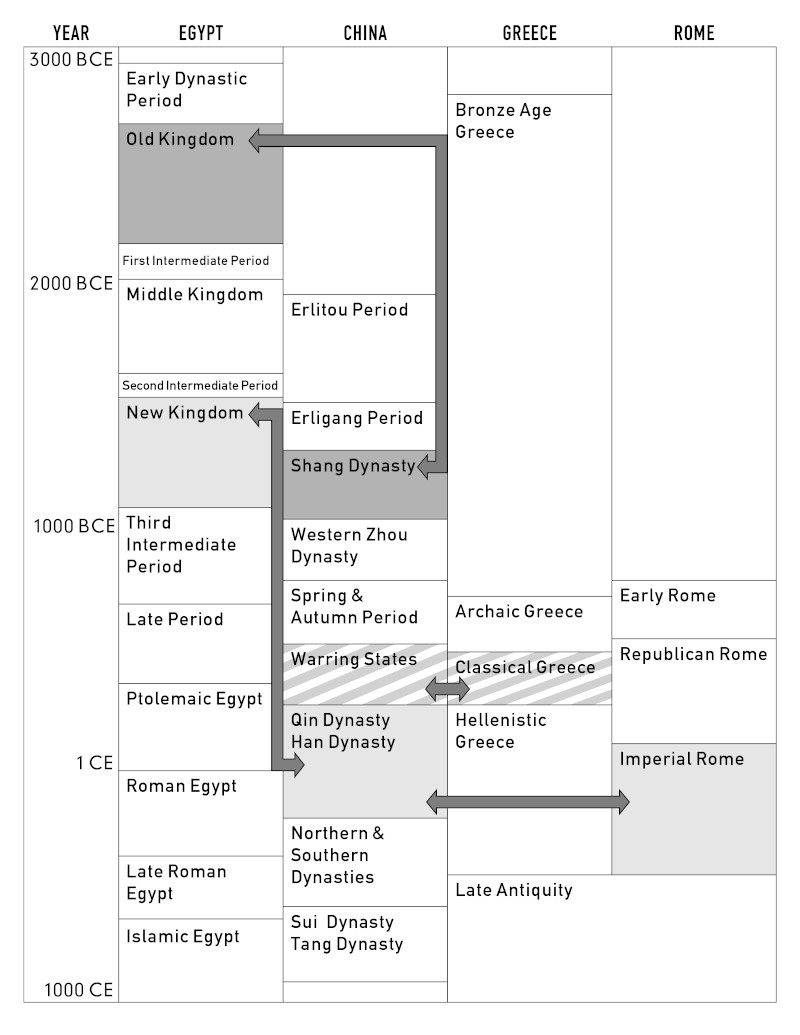
Ancient Egypt and Ancient China were two of the earliest civilizations in human history, with differences in geography, language, and cultural practices. Both civilizations share similarities in social structure, religion, and artistic contributions. Ancient Egypt had a rigid social hierarchy, with a pharaoh at the top, followed by the nobles, priests, scribes, and commoners, while ancient China had an emperor supported by a bureaucracy of officials with the royal family controlling land and the peasants forming the bulk of the population. Both ancient civilizations were known for their impressive art and architecture, with contributions that continue to influence modern cultures.
Ancient Egypt vs. Ancient China: Comparing Two Early Civilizations
Ancient Egypt and Ancient China are two of the earliest civilizations in the world. Despite the vast distance and differences in cultures, both empires share similarities in their history, politics, and societal customs. In this article, we will explore these similarities and differences between the two early civilizations.
Geography and Economy
Ancient Egypt was primarily located in the Northeastern part of Africa, along the Nile river. The Nile was instrumental in the development of the Egyptian civilization as it served as a source of fertile land, water, and transportation. Agriculture was the primary economic activity, and crops like barley and wheat were grown extensively. The Nile River also facilitated trade with other regions, including Mesopotamia, the Mediterranean, and parts of Africa.
Ancient China was situated in the Eastern part of Asia, along the Yellow River (Huang He) and Yangtze River. The Chinese civilization was mostly agricultural, with rice farming being the mainstay of their economy. The Yellow River valley was the cradle of Chinese civilization, and it was an essential source of water, fertile lands, and transportation.
Social Hierarchy and Political Organization
In ancient Egypt, there was a rigid social structure with a pharaoh at the top, followed by the nobles, priests, scribes, and commoners. The pharaoh, who was considered a divine ruler, had absolute power over the kingdom and was responsible for ensuring the prosperity of the nation. The priests were influential in religious affairs, while the scribes held administrative positions and were responsible for record keeping.
In ancient China, society was similarly structured, but the political organization differed in many ways. At the top, there was the emperor, who had both political and religious authority. The emperor was supported by a bureaucracy of officials who served as advisers, diplomats, and administrators. The royal family and nobles controlled the land and had considerable wealth and influence while the peasants formed the bulk of the population and were seen as the lowest class.
Religion and Belief Systems
Ancient Egypt was a polytheistic religion, meaning they believed in numerous gods and goddesses. The gods had both human and animal forms, and they were often worshiped in temples or cults. The Egyptians also believed in an afterlife, and they frequently preserved the bodies of the dead through mummification.
The ancient Chinese, on the other hand, had a complex belief system that centered around ancestor worship, divination, and the idea of the Mandate of Heaven. The Mandate of Heaven was a concept that stated that the emperor was divinely appointed to rule, and if he failed to maintain a just and peaceful society, then he would lose the mandate and be overthrown. The Chinese also believed in the existence of a spirit world, and people offered sacrifices to keep their ancestors happy and prevent misfortune from befalling them.
Art and Architecture
Both ancient Egypt and China were well known for their impressive art and architecture. In ancient Egypt, the pyramids were the most notable architectural monuments, built as tombs for the pharaohs. The Egyptians also created intricate paintings and sculptures, often depicting gods, goddesses, and mythical creatures. Hieroglyphics were the written language system used in Ancient Egypt and were often found in temples and tombs.
The ancient Chinese also had a unique style of art and architecture. Buddhism influenced Chinese art, especially during the Tang dynasty, which was known for its sculptures and porcelain. The Great Wall of China was a significant architectural achievement built by the Chinese, spanning several thousand miles, and was used for defensive purposes. Chinese art also includes calligraphy, painting on scrolls, and pottery.
Conclusion
Ancient Egypt and Ancient China were two of the earliest civilizations in human history, and both had a profound impact on later civilizations. Despite the vast differences in geography, language, and cultural practices, both civilizations share similarities in social structure, religion, and artistic contributions. The legacies of ancient Egypt and China continue to influence modern cultures and serve as significant historical landmarks in human history.