Mediterranean and Middle Eastern cuisines share many similarities in terms of ingredients and preparation methods, but each has distinct flavor profiles and cultural influences. Both cuisines have an abundance of fresh vegetables, seafood, and olive oil, with colorful spices and bold flavors. Mediterranean cuisine includes the food of the countries that border the Mediterranean Sea, while Middle Eastern cuisine refers to the food of the Middle East and neighboring regions. Both cuisines incorporate similar ingredients such as olive oil, vegetables, and rice, but the flavor profile of each cuisine is distinct, with Mediterranean cuisine emphasizing fresh herbs, lemon, and garlic and Middle Eastern cuisine known for its complex spice blends.
Mediterranean vs. Middle Eastern Cuisine: An Exploration of Similarities and Differences
Mediterranean and Middle Eastern cuisine are two of the world’s most popular culinary traditions. Both cuisines are characterized by an abundance of fresh vegetables, seafood, and olive oil, with colorful spices and bold flavors.
Geographic and Cultural Origins
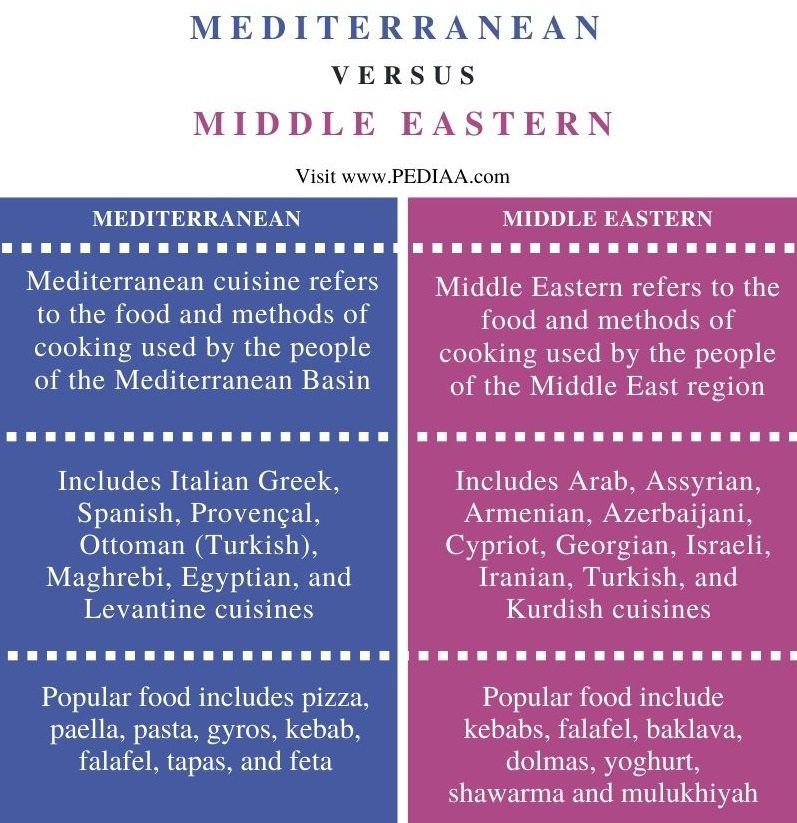
Mediterranean cuisine refers to the food of the countries and regions that border the Mediterranean Sea, including Greece, Italy, Spain, France, and North Africa. The culinary traditions of these regions have been influenced by various cultures, including the ancient Greeks, Romans, and Arabs.
Middle Eastern cuisine, on the other hand, refers to the food of the Middle East and neighboring regions, such as Turkey, Iran, and the Arabian Peninsula. The cuisine is heavily influenced by Islamic dietary restrictions and the use of spices and herbs.
Ingredients and Flavors
Both Mediterranean and Middle Eastern cuisine incorporate similar ingredients into their dishes. Olive oil is a staple in both traditions, providing a healthy fat base for cooking and flavoring salads and dishes. Vegetables such as eggplant, tomatoes, and zucchini are commonly used in both cuisines, as well as chickpeas, lentils, and rice.
While both cuisines share similar ingredients, the flavor profile of each cuisine is distinct. Mediterranean cuisine typically highlights the natural flavors of its ingredients, with an emphasis on fresh herbs, lemon, and garlic. Middle Eastern cuisine, on the other hand, is known for its complex spice blends, often featuring cumin, coriander, cinnamon, and saffron.
Meat and Seafood
Meat and seafood play a significant role in both Mediterranean and Middle Eastern cuisine. Lamb is a popular protein in both, as well as chicken and beef. While pork is a common feature in Mediterranean dishes, it is rarely found in Middle Eastern cuisine due to Islamic dietary restrictions.
Seafood is also a staple in both cuisines, with fresh fish and seafood prepared in a variety of ways. From grilled octopus to stuffed squid, Mediterranean and Middle Eastern cuisine feature a range of seafood dishes that highlight the flavors of the sea.
Bread and Pastries
Bread and pastries are a staple in both Mediterranean and Middle Eastern cuisine. In Mediterranean cuisine, bread is typically made from wheat flour, and popular types include pita, ciabatta, and focaccia. In Middle Eastern cuisine, bread is often made from sesame seeds and has a more fluffy, airy texture.
Pastries are also common in both traditions, with baklava being a popular Middle Eastern dessert and fougasse being a popular pastry in Mediterranean cuisine.
Conclusion
While Mediterranean and Middle Eastern cuisine share many similarities in terms of ingredients and preparation methods, they also have distinct flavor profiles and cultural influences. Whether you’re in the mood for fresh vegetables and herbs or complex spice blends and fluffy bread, both cuisines offer a world of culinary delights to explore.