The Byzantine Empire and the Holy Roman Empire were two significant empires in European history that played important roles in shaping the political, cultural, and religious landscape of Europe during the medieval period. The Byzantine Empire emerged in the fourth century AD while the Holy Roman Empire emerged in the ninth century AD. The Byzantine Empire was an autocratic monarchy, and the Orthodox Church played a central role in the Byzantine state, while the Holy Roman Empire had a decentralized system of governance based on the relationships between the emperor, the princes, and the papacy. Both empires had significant impacts on the legacy of Europe in terms of culture, politics, and religion.
The Byzantine Empire vs. The Holy Roman Empire: A Comparative Analysis of Two Major European Empires
Introduction
The Byzantine Empire and the Holy Roman Empire are two of the most significant empires in European history. They both played important roles in shaping the political, cultural, and religious landscape of Europe during the medieval period. While these two empires share certain similarities, there are also many differences between them. In this article, we will compare and contrast the Byzantine Empire and the Holy Roman Empire, focusing on their history, governance, culture, religion, and legacy.
History
The Byzantine Empire emerged in the fourth century AD when Constantine the Great founded a new capital in Constantinople. This city became the center of the Byzantine Empire, which lasted for over a thousand years until it fell to the Ottoman Turks in 1453. The Byzantine Empire was heavily influenced by ancient Greek and Roman culture, and it played a key role in preserving and transmitting this culture to the West.
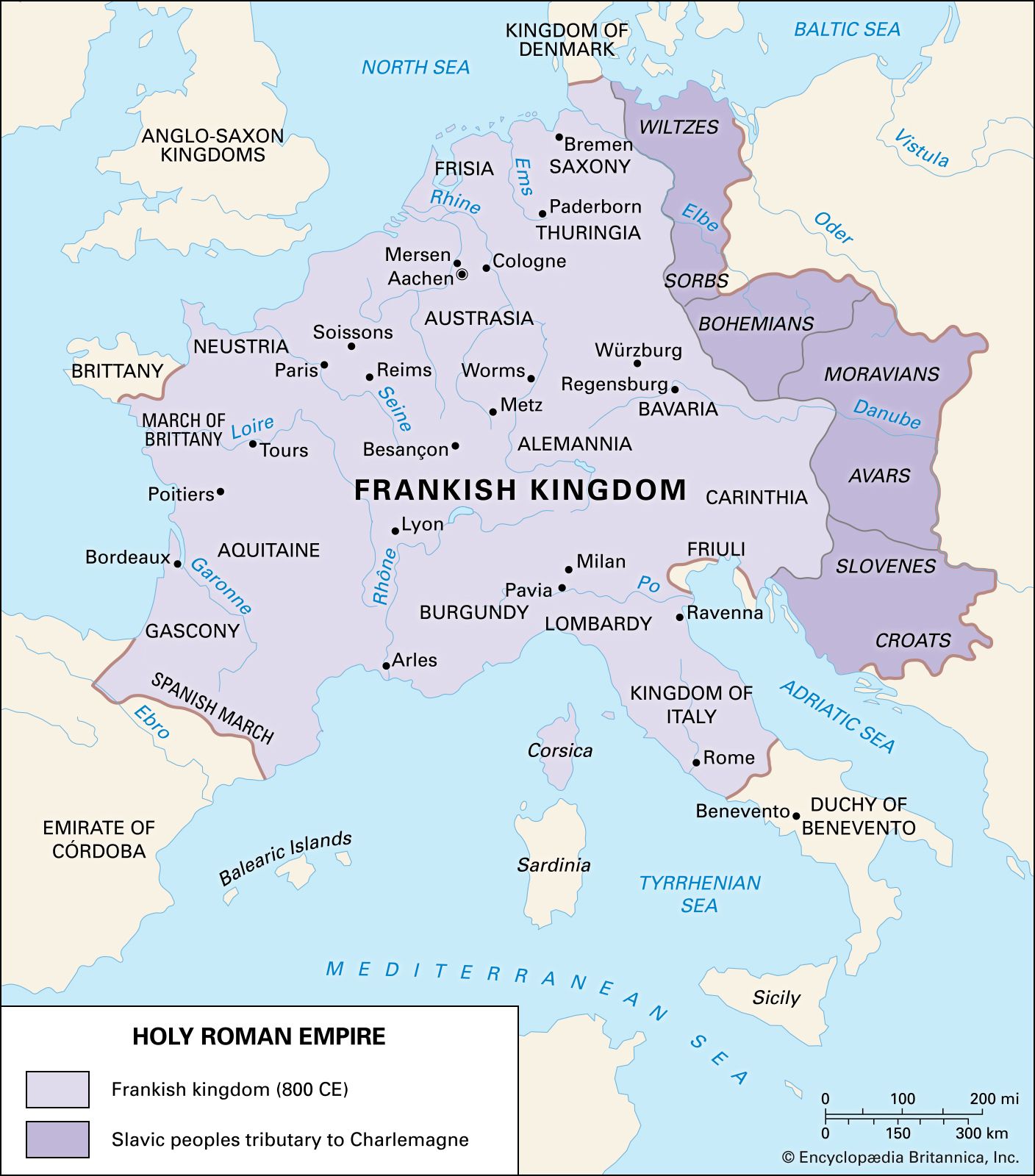
The Holy Roman Empire, on the other hand, emerged in the ninth century AD as a continuation of the Carolingian Empire. It was initially founded by Charlemagne, who was crowned as the first Holy Roman Emperor by Pope Leo III in 800 AD. The Holy Roman Empire lasted until its dissolution in 1806, and it was characterized by a complex political structure based on the relationships between the emperor, the princes, and the papacy.
Governance
The Byzantine Empire was an autocratic monarchy, with the emperor holding absolute power over the government and the society. The emperor was also the head of the Orthodox Church, which played a central role in the Byzantine state. The society was divided into two main classes: the aristocracy and the common people. The aristocracy were the elite citizens who held positions of power and influence, while the common people were the laborers and merchants who comprised the majority of the population.
The Holy Roman Empire, on the other hand, had a decentralized system of government that was based on the relationships between the emperor, the princes, and the papacy. The emperor was elected by a group of princes, who also had significant power and authority in their own territories. The papacy also played an important role in the governance of the Holy Roman Empire, as it was closely allied with the emperor and had significant influence over the religious and political affairs of the time.
Culture
The Byzantine Empire was influenced by ancient Greek and Roman culture, and it developed a unique artistic and architectural style that was characterized by intricate mosaics, gold leaf, and vivid colors. Byzantine art also featured religious themes and icons, which were used to underscore the importance of the Orthodox Church in the Byzantine state. The Byzantine Empire was also known for its literature, philosophy, and science, which made important contributions to the intellectual and cultural legacy of Europe.
The Holy Roman Empire, on the other hand, was characterized by a diverse range of cultural influences, as it encompassed a wide variety of territories and peoples. The Holy Roman Empire also made significant contributions to the development of European art, architecture, literature, and music, and it was home to many famous artists, writers, and musicians throughout its history.
Religion
The Byzantine Empire was ruled by the Orthodox Church, which played a central role in the government and the society. The emperor was the head of the Orthodox Church, and religious officials held significant power and influence in the state. The Orthodox Church was based in Constantinople, and it was closely affiliated with the Byzantine Empire throughout its history.
The Holy Roman Empire, on the other hand, was characterized by religious diversity and conflict. The empire was split between Catholic and Protestant territories, and there were many wars and conflicts fought over religious differences throughout its history. The papacy also played a significant role in the governance of the Holy Roman Empire, and there were often tensions between the pope and the emperor over issues of religious authority and influence.
Legacy
The Byzantine Empire had a significant impact on the political, cultural, and religious legacy of Europe. It preserved and transmitted ancient Greek and Roman culture to the West, and it played a key role in shaping the Eastern Orthodox tradition. The Byzantine Empire also had an important influence on the development of medieval art, architecture, literature, and philosophy.
The Holy Roman Empire also had a significant impact on the legacy of Europe. It shaped the political structure of the medieval period, and it played a key role in the development of feudalism and the concept of the nation-state. The Holy Roman Empire also played an important role in the development of European art, architecture, literature, and music.
Conclusion
The Byzantine Empire and the Holy Roman Empire are two of the most significant empires in European history, and they have left lasting legacies that continue to influence the modern world. While they share certain similarities, such as their impact on European culture and history, they are also distinct in their governance, culture, religion, and legacy. By studying these two empires, we can gain a deeper understanding of the complexities and diversity of European history, and appreciate the rich cultural heritage that has been passed down to us over the centuries.