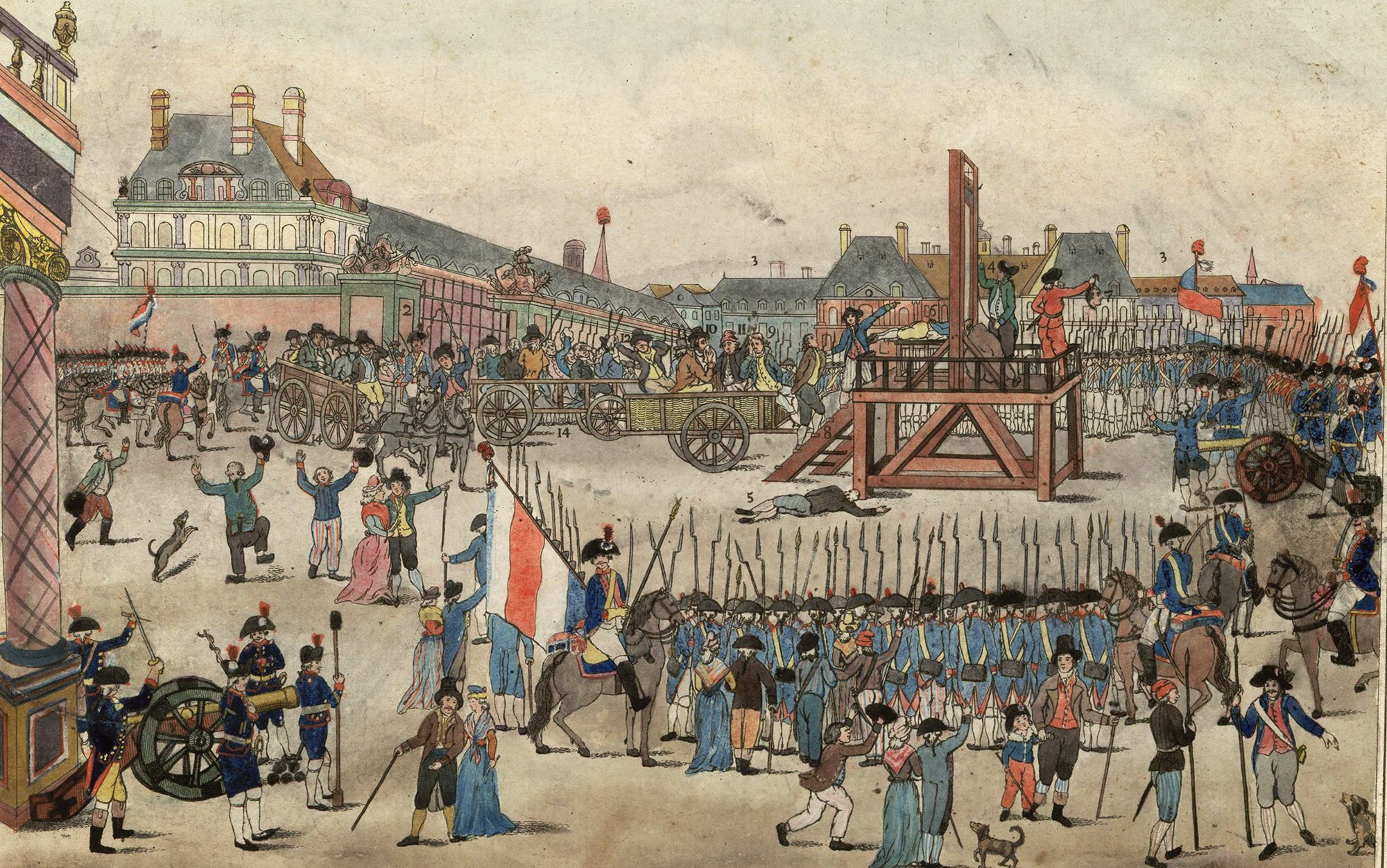
The French and American Revolutions of the late 18th century had similar goals but different paths, resulting in vastly different outcomes. The American Revolution was a success, led by George Washington and other founding fathers who espoused liberal ideals such as freedom, democracy, and human rights, resulting in the establishment of the US. In contrast, the French Revolution was violent and chaotic period, led by radical leaders, including Robespierre, which involved the brutal execution of thousands of people, and resulted in the overthrow of the Bourbon monarchy and the establishment of the First French Republic, failing to achieve social equality.
The French Revolution vs. The American Revolution: A Menacing Scenario for Change
Introduction
The French Revolution and the American Revolution were significant events that took place in the late 18th century. Both revolutions aimed to bring about change, liberty, and equality to their respective countries. However, their paths towards achieving these goals varied significantly, resulting in vastly different outcomes. In this article, we will compare and contrast the French Revolution and the American Revolution, examining their similarities and differences and exploring the reasons for their success and failure.
Background
The American Revolution was a political upheaval that took place between 1765 to 1783, culminating in the defeat of British rule and the establishment of the United States of America. The revolution was sparked by a series of events, including the imposition of taxes on the colonists without their consent and the increasing demands for self-governance. The revolution was led by founding fathers, including George Washington, John Adams, and Thomas Jefferson, who espoused liberal ideals such as freedom, democracy, and human rights.
On the other hand, the French Revolution was a violent and chaotic period that began in 1789 and ended in 1799, resulting in the overthrow of the Bourbon monarchy and the establishment of the First French Republic. The revolution was characterized by intense social, economic, and political upheaval, and it involved the brutal execution of thousands of people, including the king, Louis XVI. The revolution was led by radical leaders such as Maximilien Robespierre, Jean-Paul Marat, and Georges Danton, who advocated for egalitarianism and social justice.
Social, Economic, and Political Causes
Both the American Revolution and the French Revolution were triggered by economic, social, and political factors. In the case of the American Revolution, the colonists were angry about their lack of representation in the British Parliament and their treatment as second-class citizens. They were also frustrated by the British government’s imposition of taxes, such as the Stamp Act and the Tea Act, which they believed were unfair and oppressive.
In contrast, the French Revolution was driven by widespread poverty, social inequality, and political corruption. France was also suffering from a severe economic crisis, exacerbated by years of excessive spending by the monarchy and the growing resentment towards an already wealthy and privileged aristocracy. The French people were tired of living in a society that lacked basic human rights and access to resources, while the monarchy and aristocracy lived lavishly.
Major Events and Leaders
The American Revolution was characterized by several significant events, such as the Boston Tea Party, the Battle of Bunker Hill, and the signing of the Declaration of Independence. The revolution was led by prominent figures such as George Washington, who served as a general of the Continental Army, and Benjamin Franklin, who played a crucial role in securing financial assistance from France.
In contrast, the French Revolution was characterized by a series of tumultuous events such as the Storming of the Bastille, the Reign of Terror, and the execution of Louis XVI. The revolution was led by radical leaders such as Robespierre, who implemented a reign of terror marked by the execution of thousands of people, and Napoleon Bonaparte, who rose to power as a military dictator following the revolution.
Impact and Legacy
The American Revolution was a resounding success that resulted in the establishment of the United States of America, a country founded on the principles of democracy, liberty, and justice. The revolution inspired other nations, such as France and Haiti, to seek their own independence and freedom. It also paved the way for the Enlightenment, a cultural and intellectual movement that emphasized reason, science, and individualism.
In contrast, the French Revolution was a mixed legacy, characterized by both successes and failures. While it resulted in the establishment of the First French Republic and the abolition of the feudal system, it also led to the rise of Napoleon Bonaparte, who became a military dictator, and the brutal reign of terror, which saw the execution of thousands of innocent people. The revolution also failed to achieve its goal of creating greater social equality, as the French society remained stratified along class lines.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the French Revolution and the American Revolution were two significant events that have shaped modern history. Both revolutions aimed to bring about change and overthrow oppressive governments, but their paths and outcomes were vastly different. The American Revolution was a success that resulted in the birth of a new country founded on liberal ideals, while the French Revolution was a mixed legacy, characterized by both successes and failures. Understanding these differences is crucial for understanding the events that continue to shape our world today.